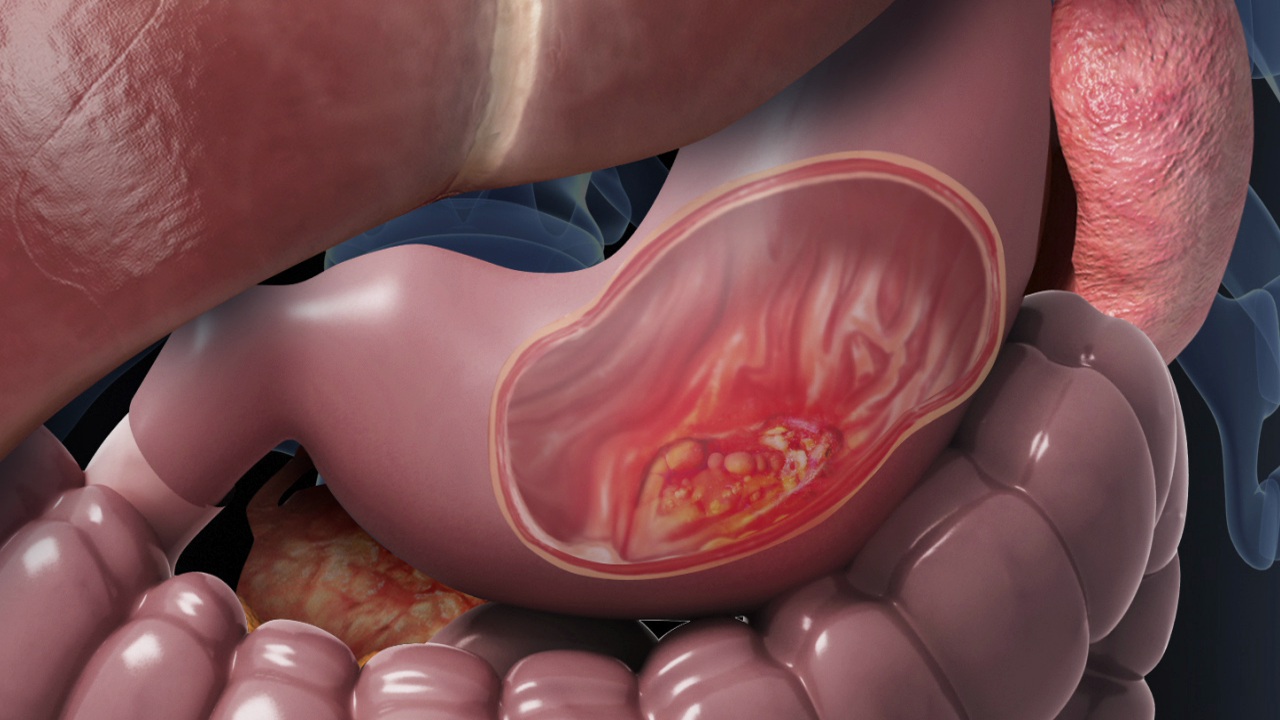
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also called gastric cancer, begins when abnormal cells grow in the stomach lining. It often develops slowly over many years. Early detection is difficult because symptoms appear late. Awareness of risk factors and regular check-ups improve survival rates.
Symptoms of Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer symptoms can resemble other digestive problems. Common signs include:
- Indigestion or persistent heartburn.
- Abdominal pain or bloating after meals.
- Loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss.
- Nausea or vomiting, sometimes with blood.
- Difficulty swallowing in advanced stages.
- Fatigue and weakness.
If symptoms last longer than a few weeks, medical evaluation is essential.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of stomach cancer is not always clear, but several factors increase risk:
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria.
- Family history of gastric cancer.
- Diet high in salty, smoked, or processed foods.
- Long-term smoking and alcohol use.
- Obesity and lack of physical activity.
- Chronic gastritis or stomach polyps.
Types of Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer can occur in different forms:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type, forming in the stomach lining.
- Lymphoma: Cancer that develops in the immune system cells of the stomach.
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): A rare type affecting connective tissue.
- Carcinoid Tumor: Grows in hormone-producing cells of the stomach.
Diagnosis of Stomach Cancer
Doctors use various tests to confirm stomach cancer:
- Endoscopy: A thin tube with a camera checks for tumors.
- Biopsy: Tissue samples confirm cancer.
- Imaging Tests: CT, MRI, and PET scans identify cancer spread.
- Blood Tests: Detect anemia or cancer markers.
Accurate diagnosis ensures proper treatment planning.
Treatment Options
Stomach cancer treatment depends on the stage and patient’s health. Common approaches include:
- Surgery: Partial or total gastrectomy to remove cancerous tissue.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that kill or stop cancer cells from multiplying.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays destroy tumors.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on proteins fueling cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer cells.
Combination therapy is often used for advanced stages.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Prevention lowers the risk of stomach cancer. Key steps include:
- Eating a diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Reducing salty and processed food consumption.
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through exercise.
- Treating H. pylori infections promptly.
- Regular screenings for people with family history.
Living with Stomach Cancer
Living with stomach cancer requires medical and emotional support. Patients benefit from counseling, nutritional guidance, and support groups. Managing side effects of treatment improves quality of life. Family involvement helps patients cope with challenges.
