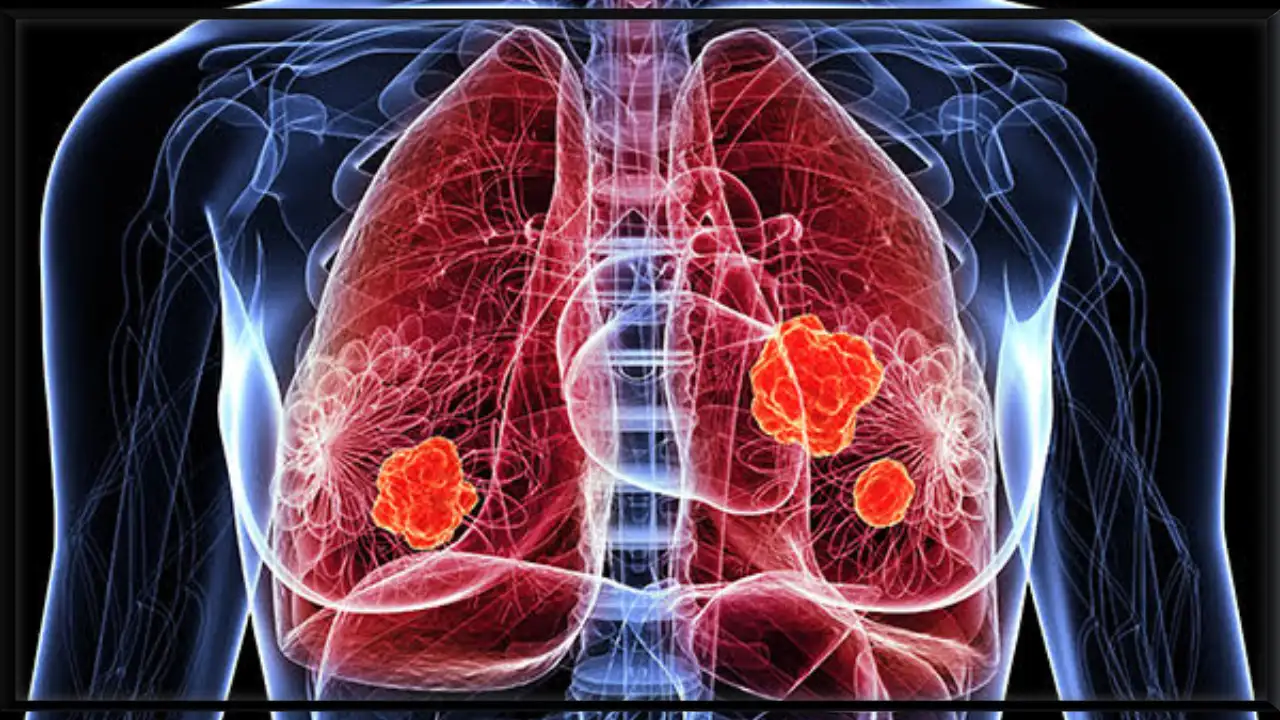
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the lungs. These cells form tumors that interfere with normal breathing. It is one of the most common and deadly cancers worldwide. Early detection plays a vital role in saving lives.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Signs of lung cancer vary and often appear in advanced stages. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough that worsens over time.
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum.
- Chest pain during deep breathing or coughing.
- Shortness of breath and wheezing.
- Hoarseness and unexplained weight loss.
- Frequent respiratory infections.
Anyone experiencing these symptoms should seek medical attention quickly.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking. However, non-smokers can also develop the disease. Major risk factors include:
- Long-term exposure to tobacco smoke.
- Inhaling secondhand smoke.
- Exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution.
- Family history of lung cancer.
- Weakened immune system and previous lung diseases.
Types of Lung Cancer
There are two main types of lung cancer:
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common type, accounting for 85% of cases.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): A fast-growing type linked strongly to smoking.
Both types require different approaches to treatment.
Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
Doctors use various methods to diagnose lung cancer. These include:
- Chest X-rays and CT scans to detect abnormal growths.
- Sputum cytology to check for cancer cells.
- Biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer.
- PET and MRI scans to determine cancer spread.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on cancer type, stage, and patient health. Common options include:
- Surgery: Removes cancerous tissue when possible.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses targeted rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Involves powerful drugs to destroy tumors.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific genetic changes in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Helps the immune system fight cancer.
Doctors may combine treatments for the best results.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Prevention remains the best defense against lung cancer. Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke. Test homes for radon gas. Wear protective equipment when working with hazardous materials. Eat a balanced diet and exercise regularly to strengthen the immune system.
Living with Lung Cancer
A diagnosis can be overwhelming, but support is available. Patients benefit from counseling, support groups, and healthy lifestyle choices. Following the treatment plan and staying active improves recovery. Emotional support from family and friends also plays a key role.
