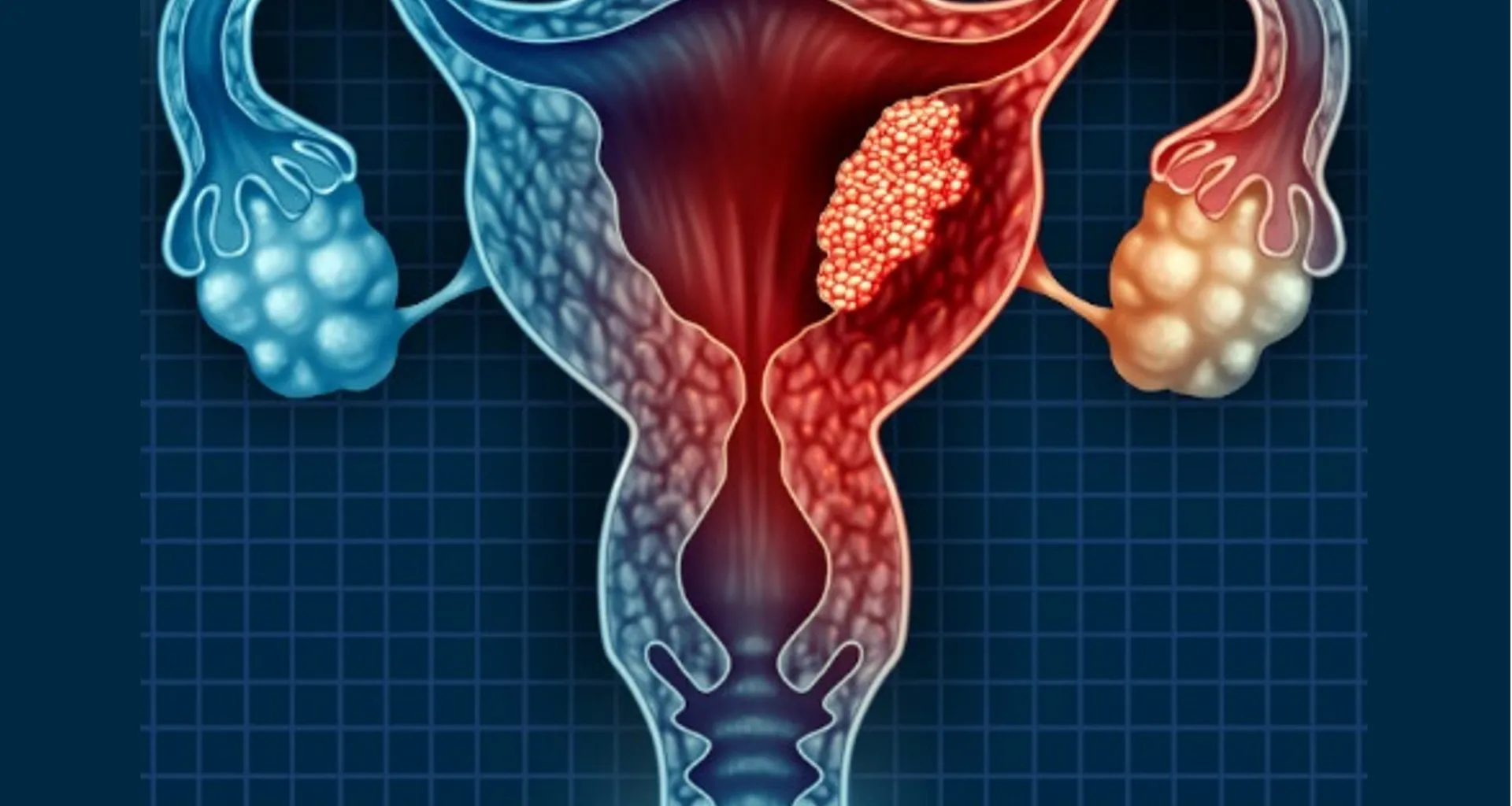
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer develops in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. It is most commonly linked to persistent infection with high-risk strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Early detection through routine screening makes treatment more effective.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer often shows no symptoms in early stages. When symptoms appear, they may include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding between periods or after intercourse.
- Unusual vaginal discharge, sometimes with a foul odor.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort during sex.
- Painful or frequent urination.
- Lower back pain or leg swelling in advanced stages.
Any persistent symptom should be evaluated by a doctor.
Causes and Risk Factors
The main cause of cervical cancer is HPV infection. However, several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- Early sexual activity and multiple partners.
- Weak immune system or HIV infection.
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives.
- Smoking and exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Family history of cervical cancer.
Types of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is classified into two main types:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Originates in the thin, flat cells lining the cervix.
- Adenocarcinoma: Begins in the glandular cells of the cervix.
Both types may occur simultaneously in some cases.
Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Screening and diagnostic tests help detect cervical cancer early. These include:
- Pap Smear Test: Detects precancerous changes in cervical cells.
- HPV DNA Test: Identifies high-risk HPV strains.
- Colposcopy: Examines the cervix using a special magnifying device.
- Biopsy: Confirms cancer by testing tissue samples.
- Imaging Tests: MRI, CT, or PET scans assess cancer spread.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage, type, and patient’s overall health. Options include:
- Surgery: Removal of cancerous tissue or, in advanced cases, hysterectomy.
- Radiation Therapy: Targets and destroys cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Uses strong drugs to kill or stop cancer cell growth.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on proteins that fuel cancer progression.
- Immunotherapy: Strengthens the body’s natural defenses against cancer.
Early-stage cervical cancer responds well to treatment with a high survival rate.
Prevention and Lifestyle Measures
Prevention plays a crucial role in reducing cervical cancer risk. Steps include:
- Vaccination against HPV at an early age.
- Regular Pap smears and HPV testing.
- Practicing safe sex and limiting multiple partners.
- Quitting smoking and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
- Strengthening immunity through a balanced diet and exercise.
Living with Cervical Cancer
A cervical cancer diagnosis may feel overwhelming. Emotional and physical support is essential for patients. Counseling, support groups, and open communication with loved ones improve coping. Adopting a healthy lifestyle and following medical guidance help recovery.
